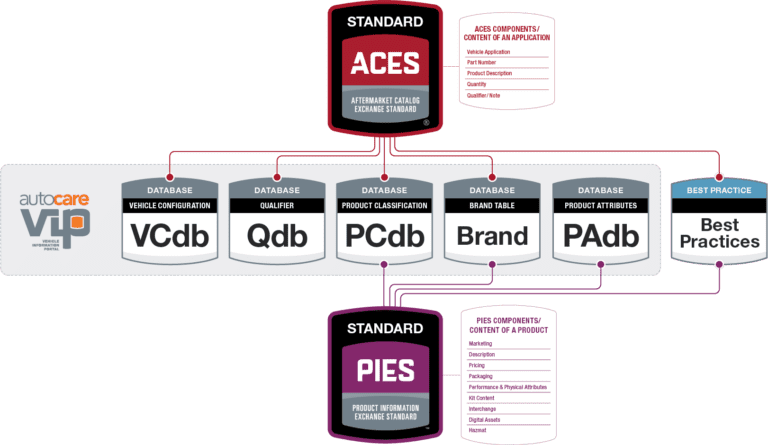
If you’re in the automotive aftermarket, you’ve likely heard the terms ACES and PIES tossed around. No, they’re not related to playing cards or desserts—they’re the industry standards that make vehicle and parts data easier to manage, track, and exchange.
ACES and PIES don’t function as standalone catalogs for looking up parts. Instead, they structure and standardize data, ensuring that manufacturers, distributors, and retailers are all speaking the same language when identifying and selling automotive parts.
Let’s break down what ACES and PIES actually do, why they matter, and how they work together to streamline the aftermarket parts industry.
ACES (Aftermarket Catalog Exchange Standard) ensures that parts fitment data—year, make, model, engine—remains accurate and consistent across platforms.
PIES (Product Information Exchange Standard) organizes product attributes, like dimensions, weight, UPC codes, and pricing, helping businesses maintain clear, detailed listings.
Together, these standards prevent miscommunication and data mismatches, making it easier for suppliers, distributors, and retailers to sell the right part to the right customer.
| ACES (Fitment Data) | PIES (Product Data) |
|---|---|
| Identifies what vehicles a part fits | Identifies what the part is |
| Uses data like year, make, model, and engine | Uses data like price, weight, and material |
| Structured through the VCdb | Structured through the PCdb |
| Helps consumers find compatible parts | Helps sellers describe product attributes |
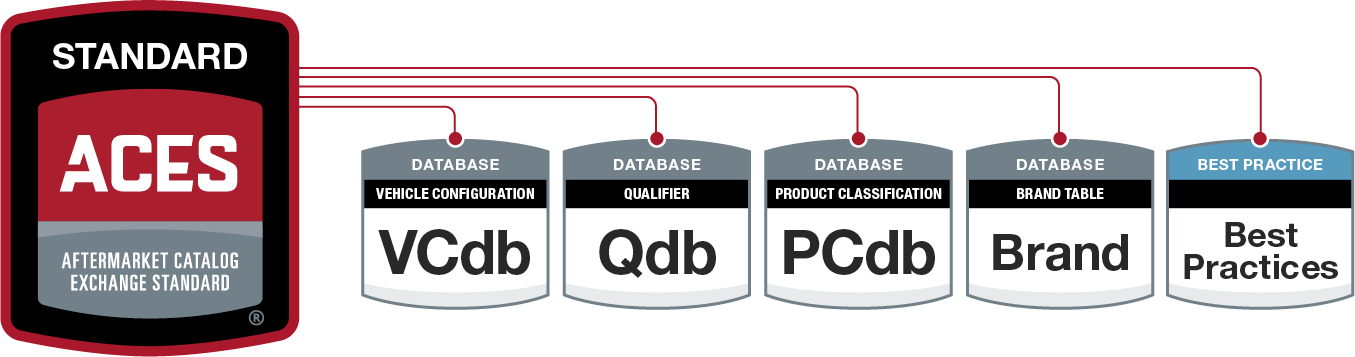
ACES is all about application fitment—or in simple terms, what parts fit which vehicles.
When a consumer searches for a part, they need to know if it’s compatible with their car. ACES organizes this data using specific criteria such as:
By standardizing fitment information, ACES eliminates the confusion of inconsistent or vague product descriptions. Instead, everyone in the supply chain—from manufacturers to online retailers—has a clear, universal format for listing vehicle compatibility.
ACES data pulls from the Vehicle Configuration Database (VCdb), which requires a paid subscription for full access. This ensures that fitment information remains accurate, up-to-date, and consistent across the industry.
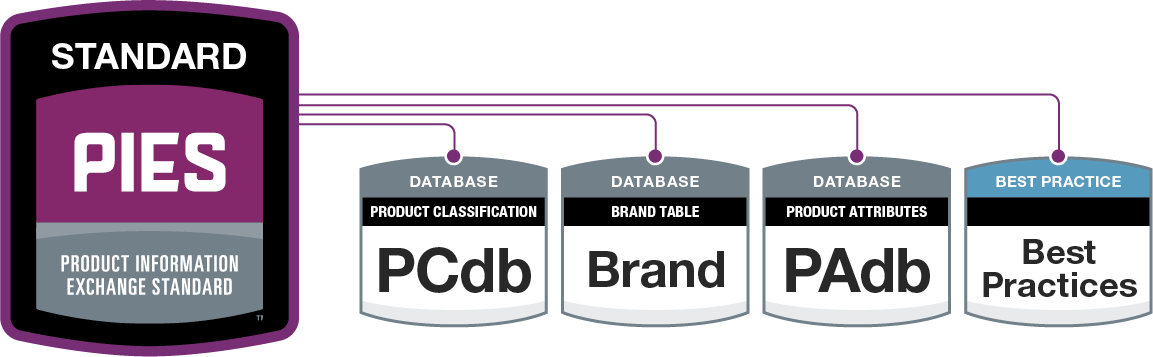
While ACES tells you what a part fits, PIES tells you what the part is.
PIES organizes product-specific details so sellers and buyers can quickly find key product attributes, such as:
Where ACES categorizes parts by function, PIES categorizes them by identity. This helps businesses ensure product listings are accurate, detailed, and optimized for both online and in-store sales.
PIES data is structured using the Product Classification Database (PCdb), another subscription-based resource that enhances data accuracy and consistency.
Without ACES and PIES, every business in the aftermarket supply chain would need to create its own unique way of categorizing products. That would lead to data mismatches, missing information, and costly errors when selling and distributing parts.
With ACES and PIES, businesses benefit from:
✅ Standardized Data: A universal format that eliminates confusion.
✅ More Accurate Listings: Consumers get the right part, every time.
✅ Faster Product Updates: Easy integration with eCommerce platforms.
✅ Better Supply Chain Communication: Smooth data exchanges between manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
These standards aren’t just a recommendation—they’re a necessity for businesses looking to scale their operations and streamline their data management.
Without ACES and PIES, businesses risk:
🚨 Incorrect fitment data → Customers order the wrong part, leading to returns.
🚨 Inconsistent product info → Confusion between suppliers and retailers.
🚨 Lost sales & bad reviews → Frustrated buyers = lost trust.
Example: A supplier using outdated spreadsheets sends incorrect fitment data to a reseller. Customers buy incompatible parts, triggering returns, refunds, and bad reviews—hurting reputation and revenue.
✅ Accurate fitment & product data → Fewer returns, better customer experience.
✅ Faster updates & integrations → Sync data across marketplaces seamlessly.
✅ Stronger supplier-retailer relationships → Everyone works with the same reliable information.
Adopting ACES and PIES isn’t optional—it’s essential for growth in the aftermarket. Standardized data protects your bottom line and ensures customers get exactly what they need.
Ready to optimize your product data? Let’s talk.
Managing automotive parts and fitment data requires structured, reliable databases that keep information consistent across the industry. That’s where the Vehicle Configuration Database (VCdb), Parts Configuration Database (PCdb), Qualifier Database (Qdb), and Product Attribute Database (PAdb) come in. These databases, managed by the Auto Care Association, form the foundation of ACES and PIES standards, ensuring that vehicle fitment, part specifications, and product details are accurate, standardized, and universally accessible.
| Database | Purpose | Role in Standardization | Impact on the Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCdb (Vehicle Configuration Database) | Stores detailed vehicle configuration data, including make, model, year, engine, and transmission. | Ensures consistent vehicle classification across platforms. | Aids in inventory management, fitment accuracy, and reducing mismatched parts. |
| PCdb (Parts Configuration Database) | Standardizes automotive part details, including part numbers, descriptions, and specifications. | Creates a uniform catalog of parts information. | Simplifies compatibility checks, inventory tracking, and reduces errors and returns. |
| Qdb (Qualifier Database) | Provides descriptive qualifiers for parts and vehicles, such as trim levels and option packages. | Adds granular details to fitment and product listings. | Enhances search accuracy, ensuring customers find the exact parts they need. |
| PAdb (Product Attribute Database) | Catalogs detailed product specifications like dimensions, weight, and materials. | Standardizes product attribute data for accurate listings. | Improves product descriptions, purchasing decisions, and reduces return rates. |

The Vehicle Configuration Database (VCdb) ensures that every vehicle’s configuration data—from make and model to transmission type—is recorded in a structured format.
Why It Matters:
✅ Prevents inconsistent fitment data across catalogs.
✅ Reduces misfits and returns by ensuring correct part-vehicle matching.
✅ Supports accurate inventory tracking and compatibility checks.

The Parts Configuration Database (PCdb) catalogs automotive part details, ensuring every component has a consistent identifier across manufacturers and distributors.
Why It Matters:
✅ Ensures accurate product descriptions across retailers.
✅ Helps suppliers and resellers track inventory and pricing efficiently.
✅ Reduces errors in cross-brand part compatibility.

The Qualifier Database (Qdb) enhances standard vehicle and parts data by adding qualifiers like trim levels, drivetrain options, and special configurations.
Why It Matters:
✅ Helps buyers filter and find parts more easily.
✅ Prevents confusion when parts only fit specific trim levels or packages.
✅ Enhances search accuracy, reducing returns from incorrect purchases.

The Product Attribute Database (PAdb) standardizes product specifications, such as dimensions, materials, weight, and packaging details.
Why It Matters:
✅ Ensures eCommerce product listings are accurate and informative.
✅ Helps businesses display precise specifications for buyers.
✅ Reduces returns from incorrect or incomplete product descriptions.

The Auto Care Brand Table is the industry-standard database for managing brand names, codes, and ownership details within ACES and PIES. It ensures that every brand is uniquely identified and standardized across distributors, retailers, and eCommerce platforms—eliminating duplicate listings, mismatched data, and brand confusion.
Without these core databases, managing vehicle fitment and product data would be chaotic. They provide:
✔ Consistent industry-wide classification of vehicles and parts.
✔ Faster data exchange between manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
✔ Improved customer satisfaction by ensuring accurate product listings.
For any business in the automotive aftermarket, leveraging VCdb, PCdb, Qdb, and PAdb is critical for maintaining accurate, structured, and market-ready data.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.